Publication – Continuous-flow reactor-based synthesis of carbohydrate and dihydrolipoic acid-capped quantum dots
Nature Protocols, 2011, Jul 28; 6 (8)
- Paola Laurino, Raghavendra Kikkeri & Peter H Seeberger
- Department of Biomolecular Systems, Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces, Potsdam, Germany & Freie Universität Berlin, Institute of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Berlin, Germany.
This paper describes a detailed protocol for the synthesis of quantum dots on a Syrris FRX flow chemistry system (now replaced by Asia). This continuous three-step synthesis generates better quality nanoparticles than traditional batch methods and is much easier to scale-up.
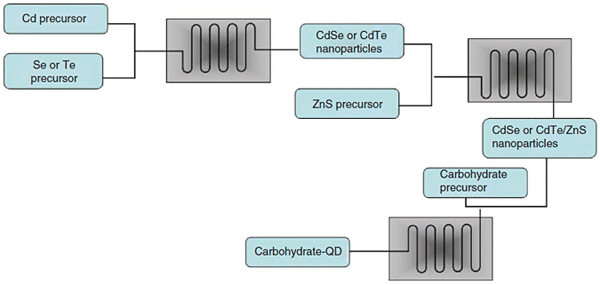
Abstract: A detailed protocol for the large-scale synthesis of carbohydrate and dihydrolipoic acid (DHLA)-coated CdSe/ZnS and CdTe/ZnS nanoparticles using continuous flow reactors is described here. Three continuous flow microreaction systems, operating at three different temperatures, are used for the synthesis of mannose-, galactose- or DHLA-functionalized quantum dots (QDs). In the first step of synthesis, the CdSe and CdTe nanoparticles are prepared. The size and spectral properties of the CdSe core of the nanoparticles are controlled by adjustment of the residence time and the temperature. As a second step, the zinc sulfide capping under homogenous conditions is carried out at a substantially lower temperature than is required for nanoparticle growth in batch processes. Finally, the trioctylphosphine/oleic acid ligand is effectively replaced with either carbohydrate PEG-thiol moieties or DHLA at 60 °C. This new protocol allows the synthesis of biologically active fluorescent QDs in 4 d.
The work published in this paper was performed on an FRX flow chemistry system (now replaced by Asia).

